You might think “mean girls,” shifting friendships, and popularity contests are a rite of passage reserved for teenagers—but the truth is, this brand of schoolyard drama starts in elementary school.
And it’s not just girls. In fact, according to a study by the University of Illinois, kids of both genders are aware of popularity issues as early as third grade. And while this survey of 12,000 elementary and middle school kids found that 41 to 48 percent of girls reported experiencing relational aggression (teasing, social exclusion, and rumor-spreading), another study actually found that it is boys who use this sort of aggression more.
So get ready, because there will likely be a day when your otherwise confident child will come home from school and tell you something that’ll make your heart sink. And while you may want to swoop in and come to the rescue (or stomp right up to the mean kid himself), experts say parents should navigate this territory carefully.
“The child is looking to us not just to solve the problem, but to know how to feel about the problem,” said Abigail Wald, a parent coach whose nontraditional coaching program, Mother Flipping Awesome, has helped more than 10,000 families, “And if we are thinking, ‘This is the worst thing to ever happen,’ that sets off alarm bells for the child and makes a mountain out of a molehill very quickly.”
And remember: the drama your kids face now can help build the resilience they’ll need later.
“One thing we can do is change our perception of these things and realize that yes they are annoying for us—and sometimes they can feel downright heartbreaking—but essentially these things are really good,” Wald said. “These are good training wheels dramas for everything that our children are going to have to deal with throughout their lives.”
Here are some scenarios to consider:
When a classmate (or friend) is mean

Before you jump to conclusions, try to help your child see the other side: maybe the “mean kid” felt hurt by something your child said to her. Maybe the child is dealing with something difficult in her own life. Or maybe you just need to teach your child to rise above the conflict. So listen—and ask questions.
“This is a beautiful opportunity for us to help our child learn values and coping skills,” Wald said. “Discuss with the child what choices the other person is making and what that child might be needing, or consider that their friend might be hurt and taking it out in these ways.”
You can also try to role-play future interactions to outfit your child for future encounters. Ask your child to play their part, while you play the part of the friend and play out different scenarios to see what options your child may have to handle the problem.
The advantage to this sort of approach, Wald said, is that even tight-lipped kids may end up showing you a lot more about what’s going on than if you had just asked them, “What happened?”
“We can also discuss whether that is somebody they really want in their life or not,” she added.
Related: Mean or Bullying Behavior – Helping Kids See the Difference
When you suspect bullying
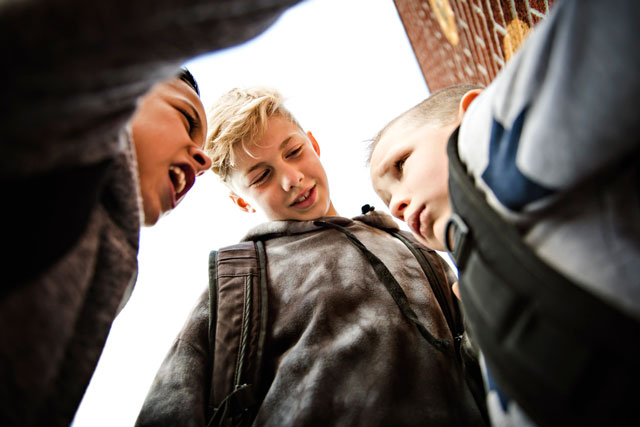

If you suspect your child may be the victim of bullying, that’s one of those times when you should definitely get involved—by more than just empathizing. (Here’s how to recognize the emotional and physical signs that your kid is being bullied, according to the National Center Against Bullying.)
Immediately reach out to the school—first your child’s teacher, then the principal—to make them aware of the situation. Most schools have strict anti-bullying policies and should attend to any suspicions immediately and respond to complaints quickly.
“If you sense that your child is having feelings of self-harm or that there is actual bullying going on—physical or emotional—that is truly unsafe, that is a time to step in to engage other adults and figure out what the options are,” Wald said.
When a good friend moves to a different “group”
While your heart might break along with your child’s, you want to resist the urge to “fix it,” just be there with your child’s feelings.
According to Sacramento psychologist Dawn Huebner, parents often rush to make things all better, but this doesn’t help kids—and can even make things worse.
“You do not want to continue to try to set up playdates if it’s clear to you that the friendship isn’t working anymore,” said Huebner, who has written several books, including Outsmarting Worry: An Older Kid’s Guide to Managing Anxiety. “Parents are quick to try to make things OK for them by solving problems or by making it seem like this thing that’s happening isn’t that bad, but when your friend doesn’t want to be your friend anymore, that’s sad. It’s normal to feel sad.”
Consequently, a parent’s first job in this situation is to empathize. Huebner urged parents to think about the sort of support they’d want. For instance, grown-ups don’t like other people solving their problems; most of the time, neither do children.
“The most helpful thing is when another person says, ‘Oh that’s hard. I’m sorry that happened,'” she said. “It’s the same for children.”
When your child isn’t picked for a team/invited to a party
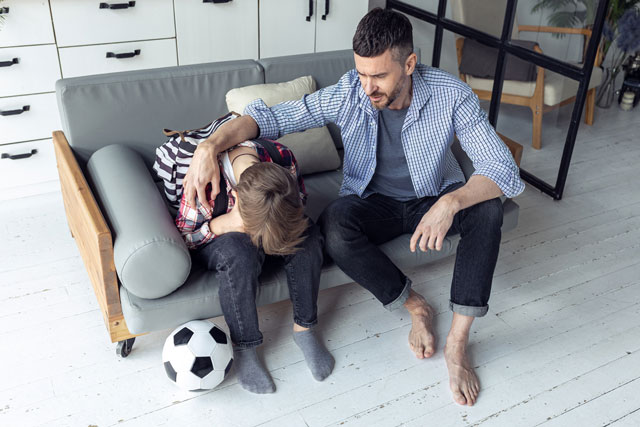

It’s hard for anyone to feel left out—and there’s nothing a parent can really do to make this feeling go away (at least not right away). But instead of trying to distract your child, experts say parents should simply sit with their children and let them feel all their feelings. Empathize, but don’t solve. This helps build coping skills for the future.
“You don’t want to distract the child to compensate; that’s a mistake,” Huebner said. “You want to start with, ‘That’s hard.’ Because sometimes we don’t have the answers. You can say, ‘I don’t know why your friend didn’t invite you. It’s hard to be left out. You’re just kind of commiserating.”
When your child doesn’t want your advice
The hardest part about watching our kids unravel over a seemingly small drama is resisting the urge to tell them what to do. After all, we may know a quick fix. Why can’t we just give them the directions?
Because, most likely, your kids don’t want your input unless they’ve actually asked you for it. So tread lightly.
“You want to hear them and be compassionate about it, but that’s different than agreeing with them,” Huebner said. “Then you can say something like, ‘Do you want to hear my ideas?’ Or, ‘Do you want some help sorting this out?'”
Related: How to Help Children Express Their Feelings at Every Age